Notes for translator:
Bighorn sheep = Borrego Cimarrón
Field Technician = Tecnico
Ecologist = Ecológo
 “It was so hot and the terrain was so steep and challenging” recalls La Paz-based bighorn sheep hunting translator Angel Antonio Marquez. “We had to stick to the shadows so the sheep couldn’t see us, making the walking even more difficult. When we were 850 yards from the ram the hunter decided to take the shot. We all thought he was crazy since it was so far and we were not at all surprised when he missed. The bullet went right between that sheep’s legs.” Angel continued, “Now this would have scared away most animals, but there was a female sheep nearby and this male was trying to be macho for her so he just stood there. The hunter got him on the second shot. 850 yards. It is the record for the farthest shot in this area.”
“It was so hot and the terrain was so steep and challenging” recalls La Paz-based bighorn sheep hunting translator Angel Antonio Marquez. “We had to stick to the shadows so the sheep couldn’t see us, making the walking even more difficult. When we were 850 yards from the ram the hunter decided to take the shot. We all thought he was crazy since it was so far and we were not at all surprised when he missed. The bullet went right between that sheep’s legs.” Angel continued, “Now this would have scared away most animals, but there was a female sheep nearby and this male was trying to be macho for her so he just stood there. The hunter got him on the second shot. 850 yards. It is the record for the farthest shot in this area.”
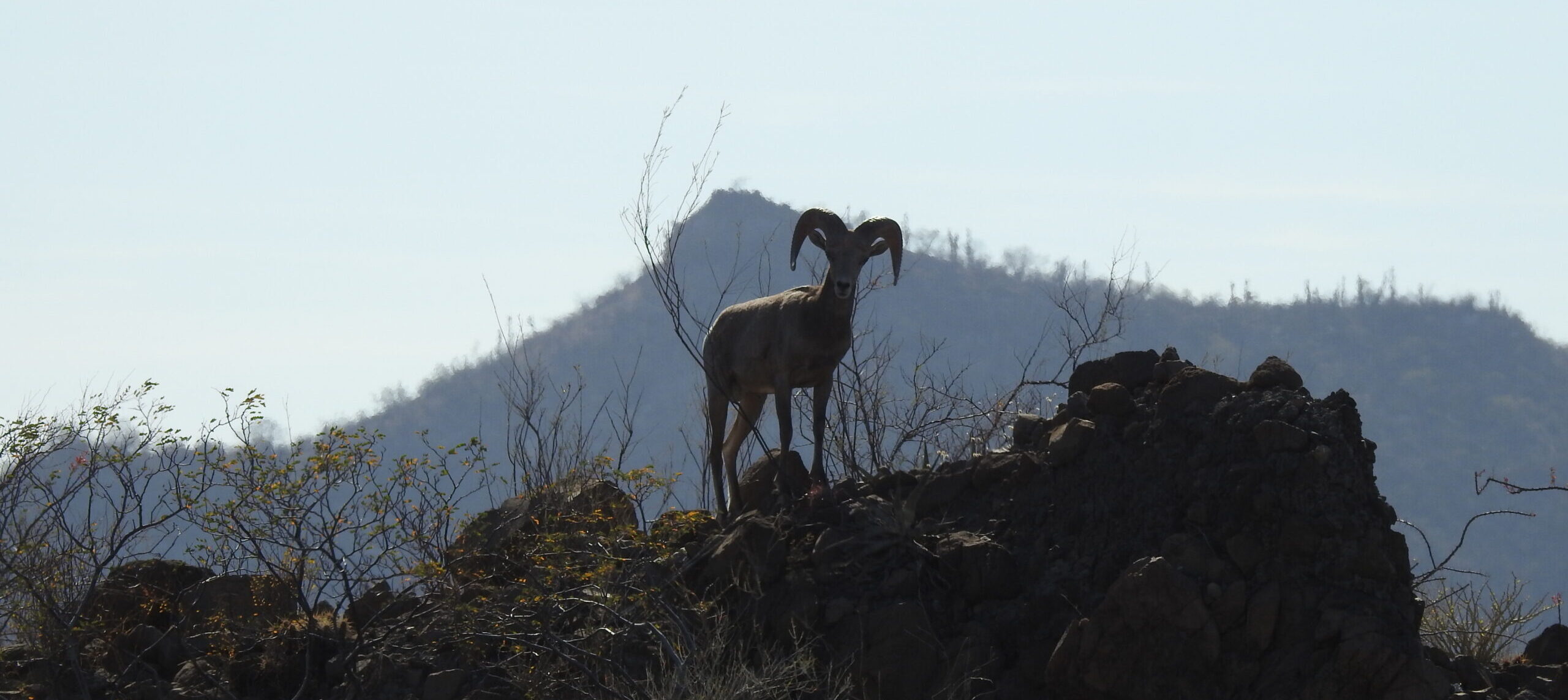
According to CONABIO, Mexico’s National Commission for the Knowledge and Use of Biodiversity, in 1800 over 1 million bighorn sheep (Ovis canadensis) roamed across the western parts of the US, Canada and northern Mexico. But the introduction of livestock and uncontrolled hunting led to a major decline, and by 1950 there were fewer than 25,000 individual sheep left. The population in northeast Mexico was extirpated and the remaining population in the northwest around Sonora and the Baja peninsula was small and fragmented. It might seem counterintuitive, but hunting is now the main activity, regulated by the Mexican government, helping to stabilize the bighorn sheep population and preserve their habitat.
“This program is an amazing idea” states Biól. Gabriela López Segurajáuregui, the Mexican CITES Scientific Authority Coordinator. “Mexico is a megadiverse country with over 10% of all species in the world. Our conservation challenge is to incentivize people to care for their resources so that they can make a living from them in an ongoing, sustainable way. Bighorn sheep trophy hunting is a major conservation success story in Mexico.”
Gabriela’s colleague M. en C. Luis Guillermo Muñoz Lacy, Chief of the National CITES implementation on Fauna Department, elaborates. “Mexico allows trophy hunting across many species, but bighorn sheep is the most valuable species for hunting in the country, meaning that hunters are willing to pay the most for those permits. The money generated by this program has a tremendously positive economic impact on local communities as well as a tremendously positive conservation impact on the sheep themselves and the lands they roam.” How much money are we talking about? Guillermo explains, “Each bighorn sheep permit in Baja California Sur (BCS) can be sold for USD 50,000 to 90,000. Sonora holds the record at USD 250,000 for one permit. BCS exports about 18 trophies per year.” In other words, it’s a game changer for the rural communities who manage the land and the hunts.
Here’s how it works. In the 1995-1997 timeframe the Mexican government created Conservation Wildlife Management Units (UMAs) to regulate wildlife harvest and non-harvest activities in Mexico, including habitat and species restoration, protection, research and environmental education. In the case of bighorn sheep, UMAs cover most of its habitat. 10 of the UMAs are in BCS and are managed by ejidos, or local communal farmers, and the remainder are across the Sea of Cortez in Sonora, Chihuahua, Coahuila and Nuevo Leon. Bighorn sheep trophy hunting is carried out within the UMA system in the states of BCS and Sonora. Baja California, the state that occupies the northern half of the Baja peninsula, does not allow hunting.
In 1975 twenty bighorn sheep were reintroduced to Tiburon Island in the Sea of Cortez off the coast of Sonora, and by 2012 that number had grown to 650. Many of those were transplanted to Sonora for repopulation and captive breeding programs and by 2019, the last year for which Sonora published its data, the continental population of bighorn sheep had recovered to 3,829 wild individuals and 4,500 in captivity. By contrast, BCS has only had a couple of reintroduction or reinforcement events and the last aerial survey conducted by SEMARNAT in 2022 estimated about 1,100 individuals in BCS.
 The UMAs of BCS pay for a team of technicians to regularly monitor the bighorn sheep population on land, participate in the hunts, and accompany the aerial surveys that are conducted every three years. The technicians are extremely clear in their minds about the value of the trophy program. “If it were not for the economic power of the trophy permits, the Bighorn sheep population would almost certainly have been decimated by now and the ejidos would have sold off most of the land” observes Ing. Antia Duarte Camacho, Field Technician of de Ejido San Jose de la Noria and Ejido Lic. Alfredo V. Bonfil. “The bighorn sheep habitat is all along the Sea of Cortez, making that land extremely valuable.” Her colleague Ecologist Miguel Angel Aguilar Juárez, Field Technician of Ejidos Ley Federal de Aguas 1, 2 and 3 adds, “By 2014 the ejidos, many of which had been impoverished, were really starting to understand the huge, sustained, economic lift flowing from the trophy program. They developed a deep appreciation for the value of the land that they own and the sheep that inhabit it. That is when they all really started working together to make the program work as a whole in BCS. Bighorn sheep move seasonally across a vast territory so corridors are important. Income from bighorn sheep hunting started motivating the ejidos to work together to maintain these huge areas with no other human activities, including the raising of livestock.” CONABIO points to the resulting large-scale habitat conservation and improved connectivity as a major achievement of the trophy hunting program.
The UMAs of BCS pay for a team of technicians to regularly monitor the bighorn sheep population on land, participate in the hunts, and accompany the aerial surveys that are conducted every three years. The technicians are extremely clear in their minds about the value of the trophy program. “If it were not for the economic power of the trophy permits, the Bighorn sheep population would almost certainly have been decimated by now and the ejidos would have sold off most of the land” observes Ing. Antia Duarte Camacho, Field Technician of de Ejido San Jose de la Noria and Ejido Lic. Alfredo V. Bonfil. “The bighorn sheep habitat is all along the Sea of Cortez, making that land extremely valuable.” Her colleague Ecologist Miguel Angel Aguilar Juárez, Field Technician of Ejidos Ley Federal de Aguas 1, 2 and 3 adds, “By 2014 the ejidos, many of which had been impoverished, were really starting to understand the huge, sustained, economic lift flowing from the trophy program. They developed a deep appreciation for the value of the land that they own and the sheep that inhabit it. That is when they all really started working together to make the program work as a whole in BCS. Bighorn sheep move seasonally across a vast territory so corridors are important. Income from bighorn sheep hunting started motivating the ejidos to work together to maintain these huge areas with no other human activities, including the raising of livestock.” CONABIO points to the resulting large-scale habitat conservation and improved connectivity as a major achievement of the trophy hunting program.
Bighorn sheep are extremely desirable among trophy hunters and are part of the sheep Grand Slam. Which leads to the question: how many sheep can you hunt without hurting the species? This is one of the critical questions that Gabriela López of the Mexican CITES Scientific Authority (CONABIO) and her team focus on. The UMAs organize to finance an aerial census of the bighorn sheep habitat every three years in the September-December timeframe. The survey is done in coordination with SEMARNAT, CONABIO and key experts. It is this survey that serves as the basis for issuing the harvest rate. Gabriela explains further, “We estimate that the aerial survey team makes visual contact with roughly 30% of the total population. As a precautionary measure we determine the number of trophy hunts that will be allowed based solely on the number of individual sheep actually observed, not the extrapolated number.” Only males that are 6 years or older can be hunted – an estimation made by the size of the horns – and the number to be hunted cannot exceed 10-20% of the observed population in each region. (The hunting guides note that hunters are not tempted by younger rams as they are going for the largest horns possible and those are, by definition, found on the oldest males. Males can live 9-12 years in the wild.) Based on the aerial survey of 2019, 18 trophy (harvest) permits were issued per year to the UMAS of BCS by SEMARNAT based on the technical and scientific advice of CONABIO. That number increased to 19 trophy permits per year based on the 2022 aerial survey. The next aerial survey will be conducted in December of 2025.
Once SEMARNAT issues the number of CITES permits to export trophies (CITES is the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora) the UMAs work with brokers based in the United States to auction off the permits in places like Las Vegas and Reno. The brokers retain 15% of the permit fee and the remainder goes to the UMA and its ejido. The UMAs would like to see the auctions moved to BCS.
 The horns and skin of the bighorn sheep shot by the hunter at 850 yards are still in the office of the technical team in La Paz. Issuance of the CITES permit for the trophy to be transported across international borders to the US-based hunter could take 3-4 months (SEMARNAT must also be consulted). CITES is a legally binding agreement between governments that works to ensure that international trade in specimens of wild animals or plants does not threaten the survival of the species. Only Mexico’s bighorn sheep population is listed on CITES Appendix II which covers species that are not necessarily threatened by international trade but that are deemed worthy of a close eye so that they do not slip into the highest category of endangerment, Appendix I. When weighing the permit to send this hunter his trophy they will carefully review, among other things, the report of the UMA technician who accompanied the hunt and took detailed notes on the geographical coordinates of where the sheep was hunted, estimated age, days taken to carry out the hunt and so forth. The technician also took biological samples for disease analysis.
The horns and skin of the bighorn sheep shot by the hunter at 850 yards are still in the office of the technical team in La Paz. Issuance of the CITES permit for the trophy to be transported across international borders to the US-based hunter could take 3-4 months (SEMARNAT must also be consulted). CITES is a legally binding agreement between governments that works to ensure that international trade in specimens of wild animals or plants does not threaten the survival of the species. Only Mexico’s bighorn sheep population is listed on CITES Appendix II which covers species that are not necessarily threatened by international trade but that are deemed worthy of a close eye so that they do not slip into the highest category of endangerment, Appendix I. When weighing the permit to send this hunter his trophy they will carefully review, among other things, the report of the UMA technician who accompanied the hunt and took detailed notes on the geographical coordinates of where the sheep was hunted, estimated age, days taken to carry out the hunt and so forth. The technician also took biological samples for disease analysis.
Gabriela, Guillermo and the technical team for the UMAs all note that trophy hunting is extremely controversial in Mexico. Even some of the very officials whose offices support trophy hunting personally speak out against it. The IUCN, the International Union for the Conservation of Nature, has long supported sustainable, properly managed trophy hunting in conservation when it provides incentives for people to conserve the trophy species and their habitats. Sacrificing a few for the many is a concept that will never unify humanity, but by the IUCN’s measure – and that of CONABIO, CITES and the UMAs – the bighorn sheep trophy program has been a success in BCS, for the species, its habitat, and for the local communities.
How the permit funds are used:
Del pago que se hace a las UMAS por la venta de los permiso para la caza de borrego cimarron el 70% es entregado a las ejidatarios dueños de las las tierras donde se encuentra la UMA y 30% es dedicado a la conservación, donde se realizan las siguentes actividades:
Actividades de conservación implementadas
Colocación de letreros, puertas de acceso
Placement of signs, gates
Censo aéreo
Aerial Census
Plan de Acción para la Conservación y manejo de las Sierras Borregueras de B.C.S.
(Con apoyo de SEMARNAT)
Limpieza y rehabilitación de aguajes
Cleaning and rehabilitation of Aguajes
Monitoreo y Vigilancia
Monitoring and surveillance
Capacitación
Training courses
Delimitación de las áreas de distribución e identificación de corredores biológicos
Delimitation of the areas of distribution and identification of biological corridors
Identificación de la problemática con la fauna feral
Identification of the problem with feral fauna
Entrega de reportes anuales a SEMARNAT
Activity Report
Construcción de corrales para el manejo de fauna feral
Construction of corrals for feral wildlife management
Programa de manejo de fauna feral
Program implementation of feral animal management
Mejoramiento de hábitat
Improvement of habitat
Diversificación de actividades: ecoturismo, cabañas, aprovechamiento cinegético de otras especies
Diversification of activities: ecotourism, cabins, hunting of other species

